Hundreds of thousands of individuals get arrested for violations relating to cannabis possession in the United States each year. Although this statistic may immediately make you think that criminal activity associated with cannabis usage is staggering, more than 90% of these arrests occurred due to people solely having marijuana in their possession. This means that almost every individual arrested for cannabis-related crimes wasn't caught selling or even using marijuana but only owning it.
Cannabis decriminalization aims to solve the issue of criminalizing an activity that is relatively benign and legal in many areas of the world. In addition, it's impossible to have a conversation about cannabis decriminalization without recognizing the impact marijuana-related offenses have on incarceration rates and how this disproportionately affects people of color.
This article aims to provide clarity on how cannabis decriminalization has a direct impact on incarceration rates.
Background on Cannabis Decriminalization

To grasp the impact that cannabis decriminalization has on incarceration rates in the United States, you must first understand what cannabis decriminalization is and how it differs from cannabis legalization.
What Is Cannabis Decriminalization?
In practice, cannabis decriminalization has varying definitions. On a national level, the possession, use, and sale of marijuana are illegal, but many U.S. states have decriminalized it.
In theory, cannabis decriminalization states that the possession of small amounts of marijuana should not get treated as a criminal offense (there is no single definition of a "small amount of marijuana"; the amount a person can possess varies by state and country). This means that many states and countries where cannabis is decriminalized treat possession of a small amount of marijuana as a "violation" rather than a misdemeanor. These violations may carry fines but do not have any legal implications.
In other states and countries where the government has decriminalized cannabis, possessing even a small amount of marijuana may be considered a misdemeanor, but the punishment may not result in jail time.
What Is the Difference Between Cannabis Decriminalization and Legalization?
Understanding the difference between cannabis decriminalization and legalization is essential to fully comprehending how much of an impact decriminalization has on incarceration rates.
In states and countries that have legalized cannabis, individuals can buy and use marijuana, and the local government regulates the system through which the public can do this. Think of cannabis legalization much like the sale of liquor; you can buy it, but where and when you can buy it varies by state. Furthermore, the state decides how much the items will be taxed, and the sale of the products gets funneled back into state funds.
While legalization allows the use and sale of recreational marijuana, decriminalization solely aims to reduce the punitive measures that cannabis consumption results in. States and countries decriminalizing cannabis possession do not necessarily allow cannabis to be sold and used, but they prevent individuals engaging in petty crimes from being incarcerated.
States and Countries That Have Decriminalized Cannabis
The decriminalization of cannabis is widespread in some regions of the world. Assessing where cannabis got decriminalized is essential in drawing parallels between decriminalization and incarceration rates.
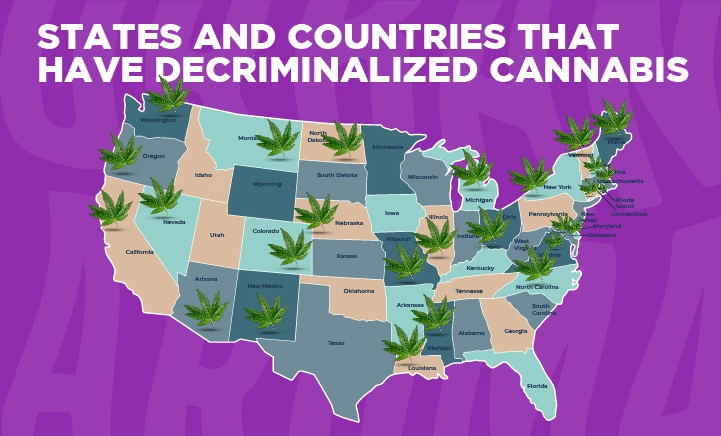
The U.S. States Where Cannabis Is Decriminalized
Below is a list of U.S. states where cannabis is decriminalized:
- Alaska
- Arizona
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia (Washington, D.C.)
- Hawaii
- Illinois
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oregon
- Rhode Island
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
An overwhelming majority of U.S. states have decriminalized cannabis, with current decriminalization reported in 31 states and Washington, D.C. However, it's essential to note that the levels of decriminalization vary widely across these states. While some states in the above list have wholly legalized cannabis, decriminalization in other states only brings lower charges associated with possessing small amounts of marijuana.
For example, let's take a look at three different states where cannabis got decriminalized and analyze how the definition of "decriminalization" changes in each of these states:
- Louisana: In Louisiana, cannabis is not legalized, which means that although individuals won't face jail time if they have 14 grams of marijuana or less, they may still be charged with a misdemeanor and have to pay a fine. Furthermore, after multiple incidences of marijuana possession, individuals may still face incarceration of up to eight years.
- Oregon: This state legalized cannabis, allowing individuals to carry up to two ounces of marijuana at any time. However, possessing more than eight pounds of marijuana is still considered a felony with a potential sentence of up to five years in prison.
- Hawaii: In Hawaii, cannabis decriminalization falls somewhere between the two previous states. Individuals can have up to three grams before being charged with a misdemeanor offense (although they may still receive a fine) but may face up to a year in prison if they possess more than an ounce.
Because cannabis is not federally decriminalized in the United States, individuals must abide by the local laws whenever they travel between states. The vast disparity in state laws regarding cannabis decriminalization may lead to complications for individuals who travel between states and may not be aware of the different restrictions in each state.
Countries Where Cannabis Is Decriminalized
Globally, cannabis decriminalization is not as widespread as it is within the United States. Although, it's important to note that on a federal level, cannabis possession is still illegal in the United States.
Below is a list of some of the countries in the world that have decriminalized or legalized cannabis:
- Argentina
- Australia
- Canada
- Colombia
- Ecuador
- Germany
- India
- Jamaica
- Malta
- Mexico
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Thailand
- The Netherlands
- Uruguay
Much like within the United States, the definition of decriminalization changes drastically amongst the countries listed above. While this is not a comprehensive list of every country where cannabis is decriminalized, it indicates that countries worldwide are beginning to trend toward decriminalization.
The Effect of Decriminalization on Incarceration Rates
Now that you understand what cannabis decriminalization is and what countries and states have enforced cannabis decriminalization, it's time to explore how it impacts incarceration rates. Below you'll find some significant facts about decriminalization, including worrying statistics about racial and socioeconomic disparities in cannabis-related incarcerations.
Noteworthy Facts About Decriminalization and Incarceration Rates
Although there are several arguments to be made suggesting that decriminalizing cannabis will positively affect incarceration rates in the United States and the world, the statistics and facts surrounding cannabis-related incarceration speak for themselves. Here's a look at some of the most staggering statistics regarding how cannabis possession gets treated in the United States:
- According to recent statistics from the U.S. Department of Justice, more than 46 percent of inmates in federal prisons got incarcerated due to being charged with drug-related crimes. The number of inmates at state prisons is lower, but they still make up more than 14 percent of the prison population.
- Although the usage of marijuana is roughly the same between Black and white people, Black individuals got arrested for marijuana-related infractions at a rate of nearly 3.75 times higher than white people.
- The United States imprisons significantly more people than any other country in the world. Although the U.S. population is only 4.25 percent of the world population, the number of incarcerated people in the United States accounts for approximately 25 percent of all prisoners across the globe.
- On average, one individual gets arrested for cannabis-related infractions every 90 seconds.
How Decriminalization Reduces the Number of People Incarcerated for Cannabis-Related Offenses
Because cannabis decriminalization is relatively new in its mainstream adoption, it's hard to measure precisely how much decriminalizing cannabis has and will continue to impact incarceration rates. However, according to an analysis released by the Congressional Budget Office, federally decriminalizing marijuana in the United States has the potential to decrease total cannabis-related prison sentences by up to 73,000 person-years between 2021 and 2030.
Based on the above statistic, it's clear that policing cannabis is negatively impacting incarceration rates in the United States. Decriminalizing marijuana would substantially reduce the number of people arrested and imprisoned for cannabis possession, especially first-time offenders.
Racial and Socioeconomic Disparities in Incarceration Rates Before and After Cannabis Decriminalization
Although it's easy to see how much marijuana criminalization impacts people of color, it's harder to measure how cannabis decriminalization will affect these groups. The current rate at which Black people get arrested over white people for marijuana possession is nearly four times higher. Because of the racial bias in policing in the United States, which gets echoed throughout the rest of the justice system, it's impossible to look at incarceration rates resulting from cannabis possession separate from racial and socioeconomic factors.
While it's difficult to find a direct link between the number of people of color incarcerated for cannabis-related offenses before and after cannabis decriminalization in dozens of states, one link is clear. Black individuals are significantly more likely to be arrested for cannabis-related crimes even after decriminalization than white people.
Because of this, decriminalization is especially important. When race is the only difference between someone being arrested or not for the same crime, it stands to reason that the actual crime is being Black and not possessing marijuana. Cannabis decriminalization is essential for addressing the inequity with which people of color get incarcerated compared to white people in the United States.
Arguments for and Against Decriminalization
Although decriminalization to some degree has already begun in much of the world, cannabis is still federally illegal in the United States and throughout the vast majority of the world. Furthermore, decriminalization can mean a myriad of things. Only because authorities would not imprison someone for possessing a small amount of marijuana that doesn't mean they can use it. At the same time, not all countries and states perceive having a "small amount" of cannabis in the same manner.
Although you may already know that cannabis legalization is a highly contested debate within the United States and beyond, is cannabis decriminalization? Take a look at some primary arguments for and against decriminalizing marijuana, and assess how these arguments may impact incarceration rates.
Arguments in Favor of Decriminalization and Their Impact on Incarceration Rates
- Cannabis decriminalization will lower incarceration rates. When nearly 50 percent of the federal prison population in the United States consists of individuals who have committed cannabis-related crimes, it's evident that decriminalization will offer a widespread reduction in the number of incarcerated individuals.
- Marijuana legalization can be highly lucrative. Tax revenue from the sale of marijuana has been proven to be extremely beneficial in states where marijuana is legal.
Arguments Against Decriminalization and Their Impact on Incarceration Rates
- Marijuana consumption can negatively impact health. Although we can't draw a parallel between this and the incarceration rates, one argument to avoid legalizing or decriminalizing marijuana is that its use can have adverse side effects.
- Cannabis decriminalization may lead to an increase in criminal activity. This theory suggests that if cannabis gets decriminalized, more individuals will partake in cannabis consumption, which may lead to intoxication and impaired judgment.
Conclusion
Cannabis-related crimes make up a massive portion of the total number of arrests in the United States (and the world) each year. Moreover, of these arrests, a considerable percentage of the state and federal prison populations are incarcerated due to cannabis-related crimes.
Decriminalization has already taken place in much of the world, and marijuana got decriminalized to some extent in more than 30 U.S. states. While this has and will continue to affect the number of imprisoned people positively, federal decriminalization is necessary to ensure individuals incarcerated on cannabis-related offenses avoid this fate.
Mass incarceration is a problem that disproportionately affects people of color in America, and the criminalization of cannabis is one of the most significant contributing factors to systemic racism within the prison system.
If you're interested in further researching cannabis decriminalization and its effects on incarceration rates in the United States and beyond, consider utilizing one or more of the following resources: